|
|
Southern Pacific Company
The Standard Time Schedules
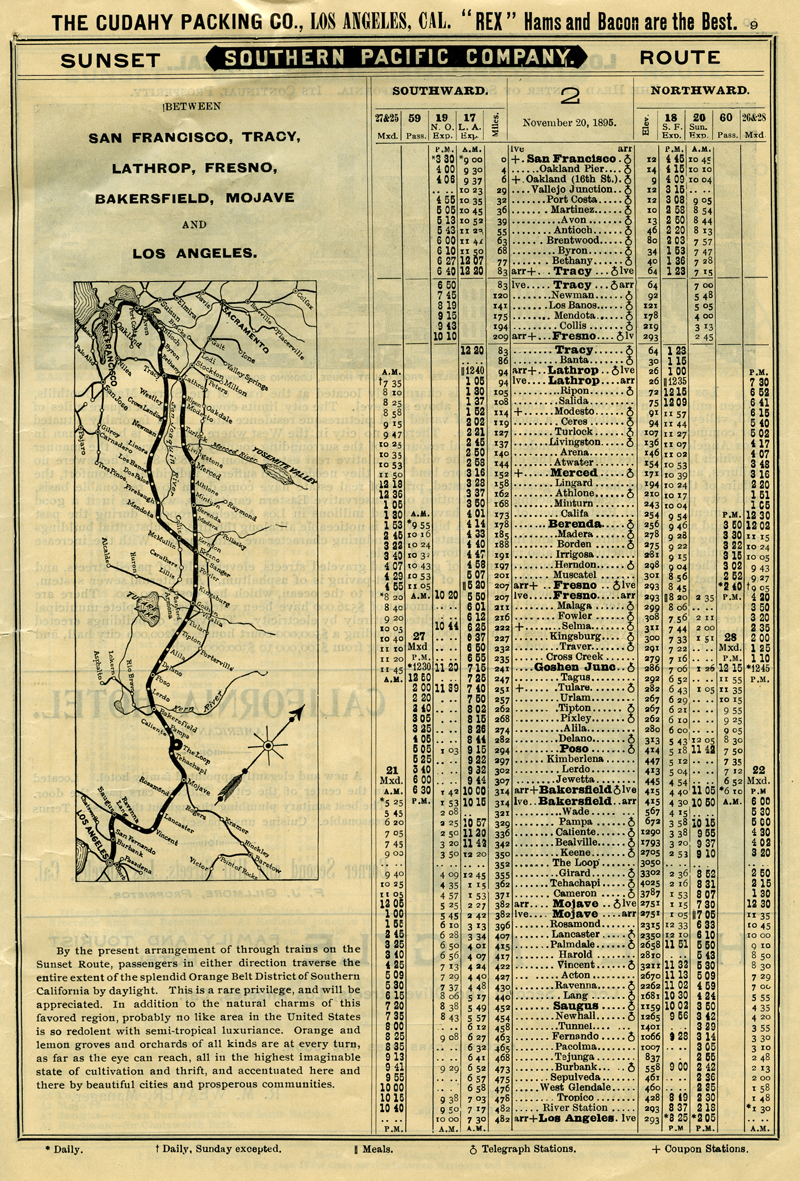
Click image to enlarge The Standard Time Schedules of All Trains Carrying Passengers on the Roads of the Southern Pacific Company and of Other Pacific Coast Railroads. Distributed Freely Each Month. November, 1895. Schedule for the Sunset Route Between San Francisco, Tracy, Lathrop, Fresno, Bakersfield, Mojave, and Los Angeles. November 20 1895. With stops at Lancaster, Palmdale, Harold, Vincent, Acton, Ravenna, Lang, Saugus, Newhall, Tunnel, Fernando, Pacoima, Tujunga, Burbank, Sepulveda, among others. "By the present arrangement of through trains on the Sunset Route, passengers in either direction traverse the entire extent of the splendid Orange Belt District of Southern California by daylight. This is a rare privilege, and will be appreciated. In addition to the natural charms of this favored region, probably no like area in the United States is so redolent with semi-tropical luxuriance. Orange and lemon groves and orchards of all kinds are at every turn, as far as the eye can reach, all in the highest imaginable state of cultivation and thrift, and accentuated here and there by beautiful cities and prosperous communities."
From The History Channel website: One of the most powerful railroad companies of the 19th century, the "Espee" (as the railroad was often called) originated in an ambitious plan conceived in 1870 by the "Big Four" western railroad barons: Collis P. Huntington, Charles Crocker, Leland Stanford, and Mark Hopkins. A year earlier, the Big Four's western-based Central Pacific had linked up with the eastern-based Union Pacific in Utah, creating the first transcontinental American railway. With that finished, the "Big Four" began to look for ways to increase their control over West Coast shipping, and decided to focus their efforts on extending the California-based Southern Pacific southward. By 1877, the Southern Pacific controlled 85 percent of California's railroad mileage. Huntington, who now dominated the company, saw an excellent opportunity to create a transcontinental line through the southern United States. Huntington had to act fast if was to beat the competition. The Texas and Pacific Railroad was already pushing westward toward the Pacific at a fast pace. Marshalling his awesome energy and financial resources, Huntington began driving his Southern Pacific line eastward. He won the race in 1881, when he linked the Southern Pacific to the Santa Fe Railroad at Deming, New Mexico, creating the second American transcontinental railway. Two years later, on February 5, 1883, Huntington gained full control of a number of smaller railroads, creating the Southern Pacific's "Sunset Route" from New Orleans to California. With the "Sunset Route," Huntington confirmed his domination over California rails. He had taken considerable financial risks to build the Southern Pacific system, and he collected very considerable financial rewards. The Southern Pacific had a near monopoly over rail service to California, and Huntington and his associates took advantage of the situation by charging high shipping rates. Termed "the Octopus" for its tentacled stranglehold on much of the California economy, the Southern Pacific inspired Californians to create some of the first strong public regulations over railroads in American history. But despite the anger and outrage Huntington's exploitation inspired, few would deny that the mighty Southern Pacific Railroad played an essential role in fostering the growth of a vibrant California economy for decades to come.
AL1976d: 9600 dpi jpeg from scan of original pamphlet, collection of Alan Pollack. |
The site owner makes no assertions as to ownership of any original copyrights to digitized images. However, these images are intended for Personal or Research use only. Any other kind of use, including but not limited to commercial or scholarly publication in any medium or format, public exhibition, or use online or in a web site, may be subject to additional restrictions including but not limited to the copyrights held by parties other than the site owner. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE for determining the existence of such rights and for obtaining any permissions and/or paying associated fees necessary for the proposed use.









