|
|
Timeline: History of Tejon Ranch
| 2014
|
Pre-1800 Studies of pre-historic times tell us the first inhabitants of Tejon Ranch included five Native American tribes. The largest area of the Ranch was inhabited by the Kitanemuk, who lived in the Tehachapi Mountains and foothills east of Castac Lake, which is now called Tejon Lake. The other tribe occupying a large area of the Ranch was the Yokuts, who occupied the San Joaquin Valley, beginning just east of Grapevine Canyon. The Ranch includes only the far western edge of former Chumash lands, but they lived at the mouth of Grapevine Canyon and along Tejon Lake. The Tataviam lived in the far western end of the Antelope Valley and had a village adjacent to the Beale Adobe. Finally, the Kawaiisu lived where the city of Tehachapi is now located, but their lands included the far northern reaches of Tejon Ranch. The first European to travel through Tejon Ranch was Capt. Don Pedro Fages from Spain in 1772. He later became governor of California under Spanish rule. The historical timeline takes us through more than two centuries of highlights that helped shape the Tejon Ranch that we know today. 1800 to 1824 1806 — Tejon gets its name from Lt. Francisco Ruiz who calls the region El Tejon, meaning badger, after his soldiers found a dead badger at the mouth of the canyon. He also names Cănada de las Uvas (Grapevine Canyon), because of the abundance of grapevines found there. 1822 — Mexico revolts against Spain. California comes under Mexican rule for 24 years. 1825 to 1849 1827 — Jedediah Strong Smith starts the flow of trappers, traders and explorers into the Tehachapi Mountain area. 1830-1833 — Kit Carson, one of the West's most noted figures, rides the range of Tejon, scouting and trapping beaver. 1837 — A bear kills Peter Lebec (Lebecque or LeBeck), a French trapper, at the site that would become Fort Tejon. 1843 — Tejon Ranch is established through Mexican land grants. 1844 — Col. John C. Fremont, Kit Carson and Alex Godey, another frontiersman, travels south over Tejon Creek Pass. 1845 — Fremont makes another trip through the area and names Kern River after Edward M. Kern, who was a topographer in his party. 1846 — Mexican American War begins. 1846 — Lt. Edward Fitzgerald Beale, eventual owner of Tejon Ranch, arrives in California as a naval officer, and serves with Fremont during the Mexican War. He is recognized as a war hero during the Battle of San Pasqual, 30 miles north of San Diego. 1848 — Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ends Spanish-Mexican rule in California. 1848 — Beale, as a Navy lieutenant, first carries the news of the discovery of gold in California to Washington. He was two months ahead of Kit Carson, who brought the news about the gold for the Army. 1849 — Beale marries Mary E. Edwards in the East. They would have three children — Truxtun, Mary and Emily. 1849 — Between 1846 and 1849, Beale makes seven trips across the country. 1850 to 1874 1850 — California is admitted as the 31st state. 1852 — Beale arrives as the Superintendent of Indian Affairs, a post he held until 1854. 1853 — Sebastian Indian Reserve is established on 75,000 acres and is home to between 500 and 800 Indians. 1853 — Early California bandito Joaquin Murrieta is said to have a silver and copper mine in the Tehachapi Mountains, which he worked with imported slave labor. 1854 — Native Americans build the first canal in Kern County to irrigate wheat on the reserve. 1854 — Fort Tejon is established by the First Dragoons at the recommendation of Beale. About 225 troops live at the Fort, which includes 15 buildings built at a cost of more than one-half million dollars. 1854 — Stagecoach stop is established at Fort Tejon with service to San Pedro (Fort Banning). Road is built from Los Angeles to the Sebastian Indian Reserve. 1855 — Rancho La Liebre is deeded to Mary Edward Beale from William C. Walker, and is the first of four Mexican land grants that would eventually make up Tejon Ranch. 1857 — Rose Station becomes a trading post and water stop for stagecoaches as well as the center for social activities in the Tejon area. 1858 — Butterfield Overland Stage establishes two stations on Tejon Ranch, one at Fort Tejon and one at the "Sink of Tejon" (Comanche Point). The route from Bakersfield to Los Angeles via Fort Tejon was 150 miles, and took 32-1/2 hours, according to the schedule. 1860 — Telegraph service from Los Angeles to San Francisco commences and passes through Fort Tejon. 1861 — Beale is appointed surveyor general for California and Nevada. 1862 — Sebastian Indian Reserve is abandoned. 1864 — Fort Tejon is abandoned on Sept. 11. 1865 — Beale purchases Rancho el Tejon and Rancho los Alamos y Agua Caliente, two of the four Mexican land grants that make up Tejon Ranch. 1866 — Kern County is established with Havilah as the county seat. 1866 — Beale buys Rancho de Castac, the last of the four original Mexican land grants that make up Tejon Ranch. Together, the grants were bought for approximately $90,000. 1868 — The Cross and Crescent is recorded in Kern County as a brand. The configuration of the Christian cross and the Muslim crescent on a brand is traced back to Old Spain as early as 997 A.D. Spanish conquistadors brought the brand to Mexico and their descendants then carried the brand to Tejon Ranch. 1873 — Bakersfield incorporates as a city. 1875 to 1899 1876 — President Ulysses S. Grant appoints Beale as minister to Austria-Hungary. 1876 — Southern Pacific Railroad is completed through Tehachapi Pass. Beale Station is established. 1879 — At the direction of Beale, Jose Jesus Lopez, Tejon Ranch sheep foreman and cattle boss for 50 years, makes legendary drive to Green River, Wyoming, starting with 17,000 sheep. After undergoing numerous challenges over uncharted desert trails, he arrived with 8,500 sheep. Beale later described the daring but costly drive: "the great disaster to our sheep." 1880 — Beale returns to California and turns to raising cattle. 1893 — Beale dies at the age of 72. Management of the Ranch passes on to his son, Truxtun Beale. 1895 — Community of Lebec is founded. 1893 — Sequoia National Forest is created by proclamation of President Benjamin Harrison. 1899 — Oil is discovered in Kern County. 1900 to 1924 1900 — Beale Memorial Library opens in Bakersfield, the first free library in Kern County. 1904 — Truxtun Beale presents the Beale Clock Tower, located at the intersection of Chester and 17th Street, to the City of Bakersfield as a memorial to his mother. The 64-foot clock tower featured a Moorish design. 1912 — A group of businessmen, led by Harry Chandler and M.H. Sherman, buys Tejon Ranch from Truxtun Beale. 1915 — The Ridge Route, considered at the time to be one of the most scientifically built mountain roads in the world, opens. 1925 to 1949 1936 — Tejon Ranch Company is incorporated. 1936 — A new three-lane road replaces the original tortuous Grapevine Grade on the Ridge Route. 1939 — Tejon Ranch donates land to the State of California to establish the Fort Tejon State Historical Park. 1943 — Tejon Ranch celebrates its 100th anniversary. 1950 to 1974 1952 — Major earthquake strikes with Tehachapi at its center. Among the casualties are the Beale Library and Beale Clock Tower in Bakersfield. The old ranch headquarters also suffered severe structural damage. 1952 — A four-lane expressway (Highway 99) replaces the three-lane highway through the Grapevine. 1955 — Tejon Ranch's board of directors authorizes an initial appropriation of $275,000 to build a headquarters and housing for ranch personnel at its current site across Interstate 5 from Fort Tejon. 1957 — Tejon Ranch donates 3 acres for El Tejon School, bringing the total ranch donation of land for the school site to 10 acres. 1963 — Construction begins on the eight-lane freeway that would become Interstate 5 through Tejon Ranch. 1965 — Construction begins on the A.D. Edmonston Pumping Plant, largest pumping facility of the California Aqueduct, also known as the State Water Project, to lift water almost 2,000 feet up and over the Tehachapi Mountains into Southern California. At peak capacity, the plant pumps almost 2 million gallons a minute through 10 miles of underground pipeline across the Tehachapi Mountains on Tejon Ranch. 1971 — Gov. Ronald Reagan starts the first pump at Edmonston Pumping Plant on Tejon Ranch, as part of a ceremony celebrating the first water deliveries to Southern California via the California Aqueduct. 1973 — Tejon Ranch Company shares begin trading on the American Stock Exchange. Previously, they had been traded over the counter. 1975 to 1999 1991 — The Umbrellas, a temporary work of art by Christo and Jeanne-Claude, opens along an 18-mile stretch of Interstate 5 between Gorman and the Grapevine. More than 1,700 umbrellas are displayed on Tejon Ranch and other private and government-owned land for 18 days.
1993 — Tejon Ranch marks its 150th anniversary. 1996 — Robert A. Stine becomes chief executive officer of Tejon Ranch Company. 1999 — Tejon Ranch Company shares begin trading on the New York Stock Exchange. 1999 — The 51-acre Petro Travel Plaza opens at the junction of Interstate 5 and Highway 99, providing needed services to travelers and the trucking industry. 1999 — Tejon Ranch initiates three new development projects:
2000 to Date 2000 — Construction begins on IKEA's Western North American Distribution Center on an 80-acre site in the Tejon Ranch Commerce Center. 2003 — Tejon Ranch announces its vision for the future of the Ranch, which includes significant conservation, a continued commitment to historic ranching and farming operations and the environmentally sensitive development of a limited portion of the Ranch. 2004 — Tejon Ranch announces a plan to create a Habitat Conservation Plan for the California condor, including a 37,000-acre condor study area. 2007 — At the urging of condor experts, Tejon Ranch Company announced a ban on the use of lead ammunition on the Ranch. Tejon Ranch operates California's largest and finest private hunting program. 2008 — Tejon Ranch Company and top environmental resource groups — the Sierra Club, NRDC, California Audubon, Planning and Conservation League and Endangered Habitats League — announce landmark agreement to protect as much as 240,000 of Tejon Ranch for future generations. The agreement, which would conserve up to 90% of the Ranch, is the most significant private conservation achievement in California history. 2008 — The Habitat Conservation Plan expands to include 27 plant and animal specials and is renamed the Tehachapi Uplands Multi-Species Habitat Conservation Plan. 2009 — Tejon Ranch receives California's most prestigious environmental honor, the Governor's Environmental and Economic Leadership Award. 2009 — A new national veteran's cemetery, the Bakersfield National Cemetery, opens on a 500-acre site donated by Tejon Ranch. 2009 — Kern County Board of Supervisors approve Tejon Mountain Village. 2009 — Famous Footwear opens distribution center at Tejon Ranch Commerce Center.
2012 — Caterpillar Inc. begins construction of a 400,000-square-foot parts distribution center at the Tejon Ranch Commerce Center.
2012 — Dollar General begins operations at the Tejon Ranch Commerce Center. 2013 — Construction begins on The Outlets at Tejon Ranch, a 325,000-square-foot retail outlet center.
|
Beale Residence, Photo 1888-1900
Santa Fe Railroad Plan 1890
Wild Grape Vines ~1890
Cowboys 1902
Sale to L.A. Times Syndicate 1912
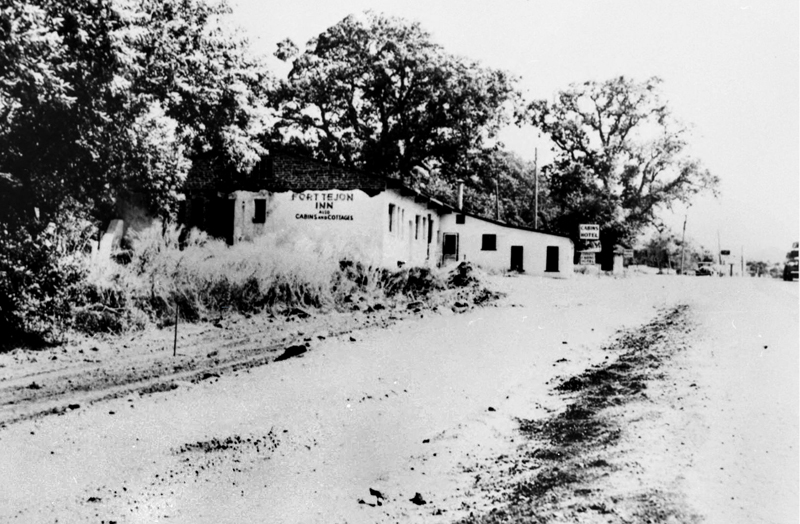
Fort Tejon Inn ~1940
Rose Station 1941
Tejon Trout Lakes 1950s (Mult.)
HQ Ruins 1968
|
The site owner makes no assertions as to ownership of any original copyrights to digitized images. However, these images are intended for Personal or Research use only. Any other kind of use, including but not limited to commercial or scholarly publication in any medium or format, public exhibition, or use online or in a web site, may be subject to additional restrictions including but not limited to the copyrights held by parties other than the site owner. USERS ARE SOLELY RESPONSIBLE for determining the existence of such rights and for obtaining any permissions and/or paying associated fees necessary for the proposed use.