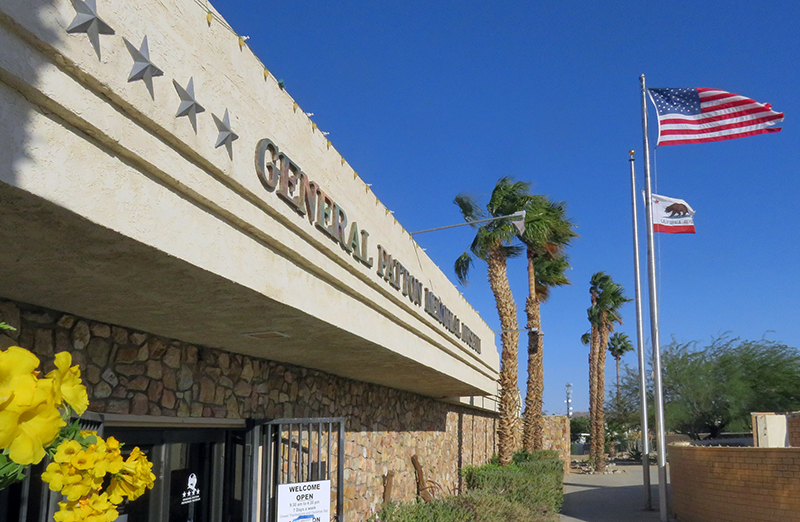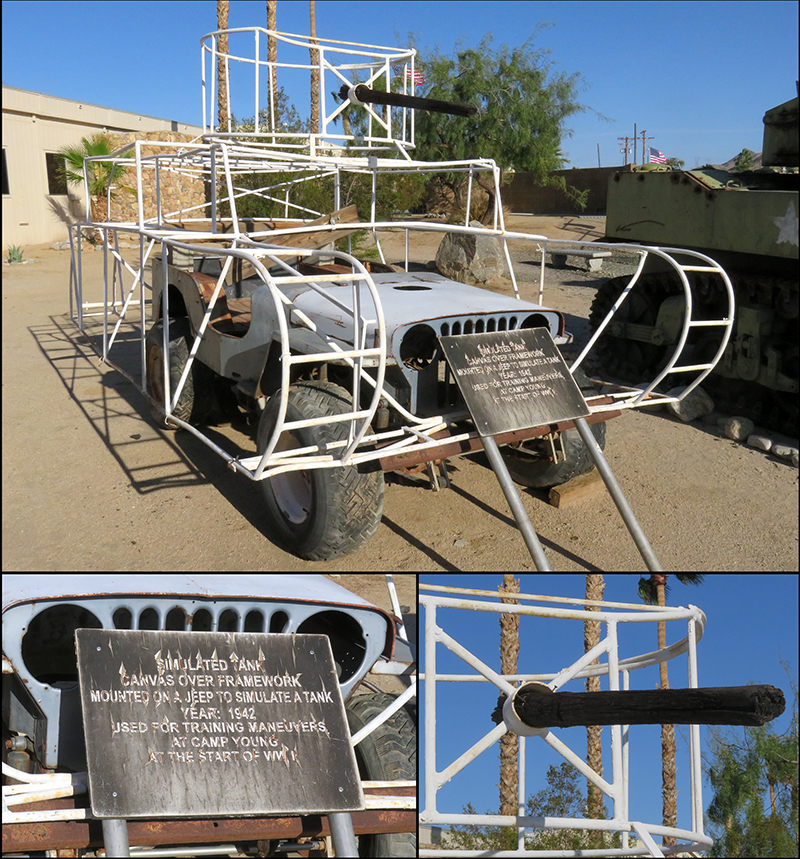
Have you ever traveled on I-10 between the California-Arizona border and Palm Springs and stopped for gas at Chiriaco Summit and wondered why there was a General Patton Memorial Museum there — in the middle of our desert? If you have never stopped there, I recommend that you do.
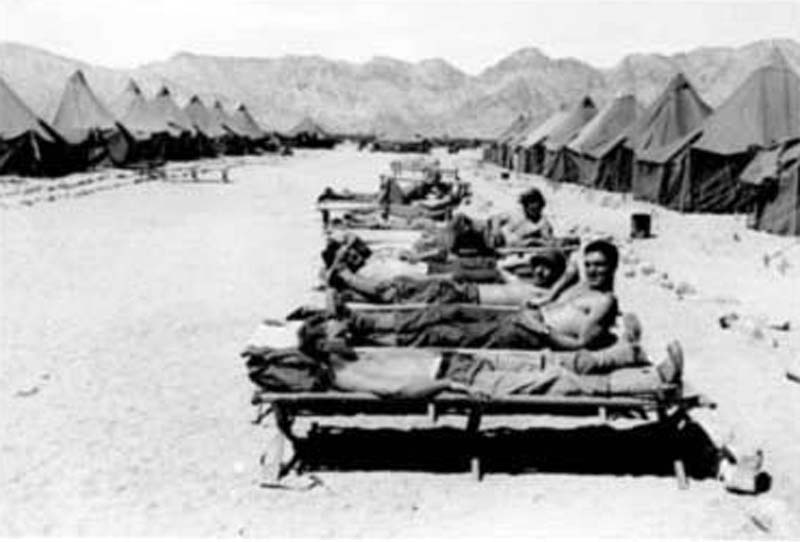
The reason the General Patton Memorial Museum is in Chiriaco Summit is because during World War II, the headquarters of an important military training ground was located there. The area was known as Camp Young and was the world's largest Army post.
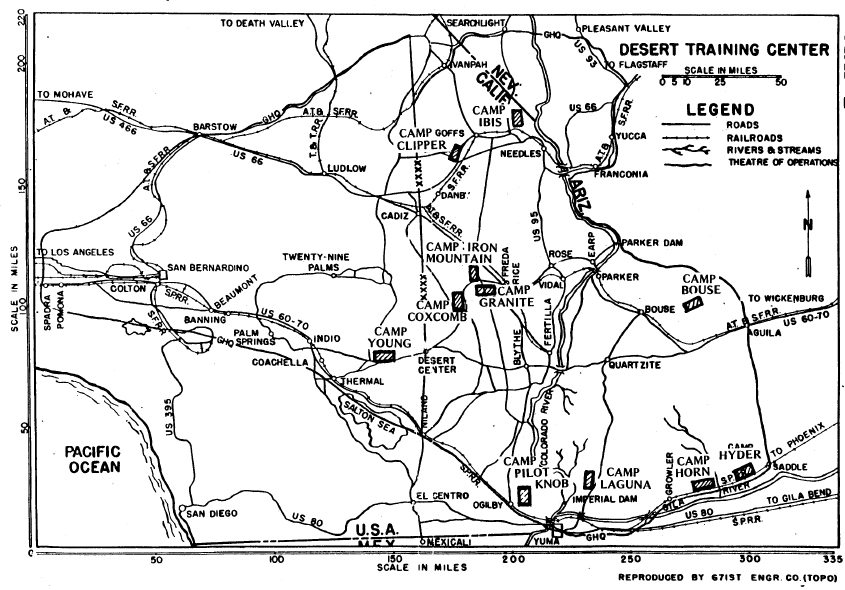
In the earliest days of World War II, the U.S. War Department recognized that training our troops under harsh conditions could make them better suited to withstand battle in rugged terrain and inhospitable climates. For that reason, in 1942 it created the Desert Training Center, California-Arizona Maneuver Area (DTC-CAMA). The Desert Training Center was the largest military training ground in the history of military maneuvers, which led to U.S. victories in the hot, arid lands of North Africa, the mud and mire in Europe, the ice and snow of Alaska, and the Pacific jungles.
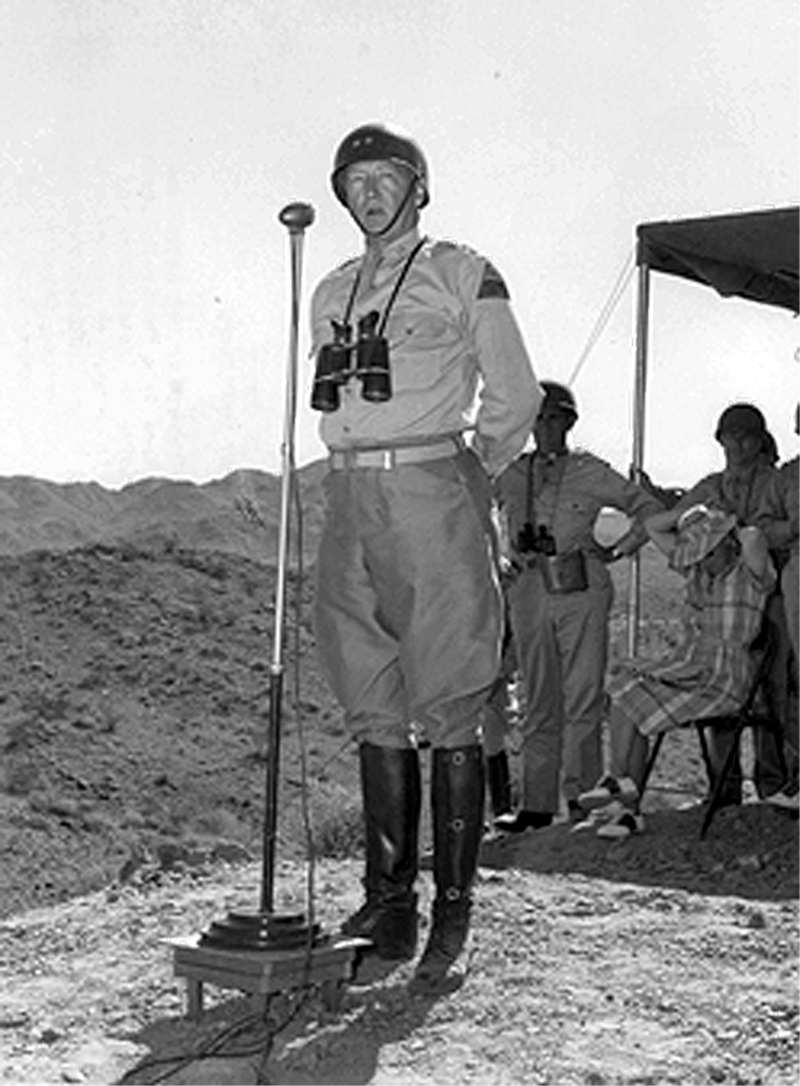

Patton reviews troops at Camp Young, June 4, 1942 | Click to enlarge.
|
Maj. Gen. General George S. Patton Jr. came to Camp Young as the first commanding general of the Desert Training Center. His first orders were to select other areas within the desert that would be suitable for the large-scale maneuvers necessary to prepare American soldiers for combat in the North African desert. Under his direction, 10 other camps were established throughout California, Arizona and Nevada. A total of seven were located in California.
In early 1942, Patton told his troops:
"The war in Europe is over for us. England will probably fall this year. Our first chance to get at the enemy will be in North Africa. We cannot train troops to fight in the desert of North Africa by training in the swamps of Georgia. ... The California desert can kill quicker than the enemy. We will lose a lot of men from the heat, but training will save hundreds of lives when we get into combat."
Maneuvers typically consisted of divisions (about 15,000 men each), fighting each other in mock battles. The infantry and armored divisions traveled over the open desert, making their own roads and paths.
Patton commanded the Desert Training Center from March to August 1942, at which time he was sent to North Africa to fight the Germans. Various commanders ran the Desert Training Center until its close in 1944.
The camps were closed when it became clear the Allies would win the war. The military removed most of the structures at the camps but left much of the infrastructure, such as a large relief map at Camp Iron Mountain, flag circles, tent areas, staging areas, rock-lined roads, as well as food cans, gas and oil cans, and shell casings.

Camp Iron Mountain is the best-known and -preserved Patton military camp. Camp Iron Mountain is located at the southern edge of the Iron Mountains, which abut the eastern side of the Cadiz Valley just north of current-day Highway 62.
Camp Iron Mountain was established in 1942. It is likely many maneuvers were planned at Camp Iron Mountain, with the benefit of its large relief map that measured 200 feet by 75 feet. The relief map, built by the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers, depicted the entire DTC-CAMA training area from about Kingman, Ariz., to Twentynine Palms, and from about Hoover Dam to the Coachella Valley. The map, which was built to scale, included a wooden walkway that spanned the distance of the map, and small wooden signs that identified the 10 divisional camps and large topographic features.
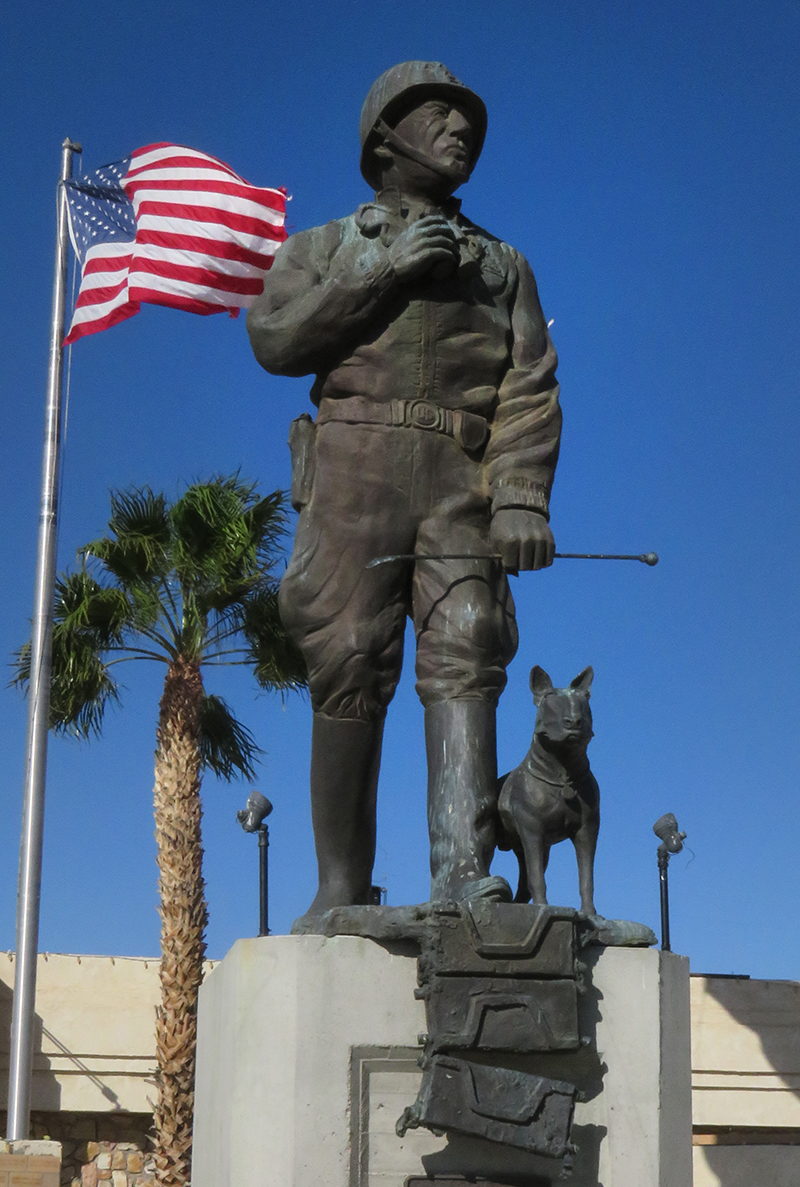

Patton monument at Chiriaco Summit | Click to enlarge.
|
When one visits Camp Iron Mountain today, one can readily see two alters, rock mosaics, and rock alignments along roads, despite harsh weather conditions and vandalism. Unfortunately, the large relief map is no longer visible today; the walkway was seen as late as 1977. Even in the late 1970s, artifacts still could be found in large numbers.
Prior to the establishment of California Highway 62, the Iron Mountain area was extremely isolated, which protected the camp from the level of vandalism it currently faces. Sadly, over the years, selfish and thoughtless visitors have stolen most of the remains that were easy to carry.
In 1973, portions of Camp Iron Mountain were made a preserve. In 1979, a fence and interpretive sign were erected around the area, but the sign was soon vandalized. In 1980, the Bureau of Land Management designated the region an Area of Critical Environmental Concern to protect its historical values.
Today, the BLM is charged with managing the public lands on which all of the camps lie. The BLM has made a concerted effort to preserve the remaining features, but lack of resources has left the camps vulnerable.
Unfortunately, the BLM's efforts have become increasingly challenging, as Congress has continued to reduce funding to the Department of Interior (of which the BLM is a component). Asking your congressional leaders to stop reducing the funding given to the Department of Interior could help the BLM with its conservation efforts. The BLM needs sufficient resources in order to better protect these camps that are such an important part of our state and nation's history.
Linda Castro is the Desert Field Organizer for the California Wilderness Coalition and serves on the board of the SCV-based Community Hiking Club.
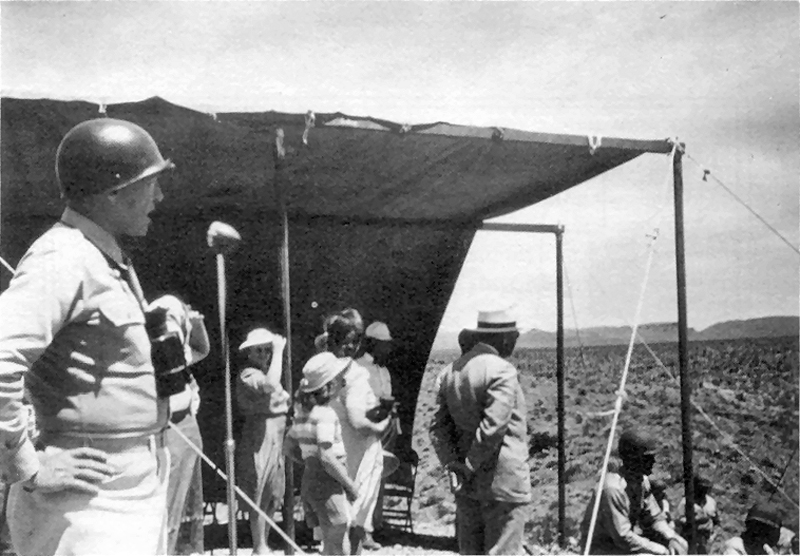

Patton reviews troops at Camp Young, June 4, 1942.


















